A Drop of Blood, An Early Warning: New Hope for Predicting Alzheimer's in the Aging Population
With the accelerating global aging process, Alzheimer's disease and related cognitive disorders have become a major challenge to human health. According to statistics, there are over 55 million dementia patients worldwide, with approximately 60%-70% caused by Alzheimer's disease. However, due to limited diagnostic methods, the true prevalence has long been underestimated, especially in the elderly population.
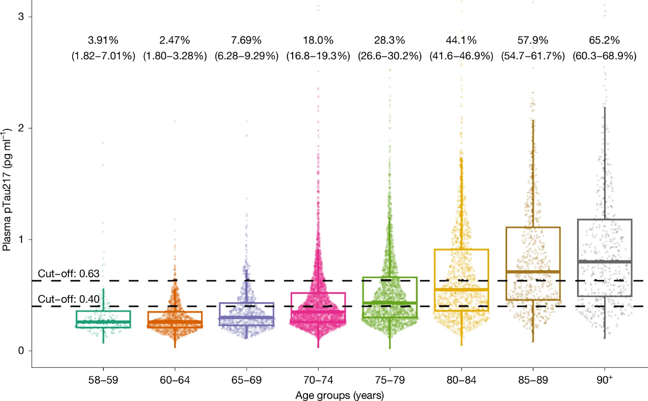
Higher Age, Higher Prevalence
Previously, diagnosing Alzheimer's disease-related pathological changes typically required obtaining cerebrospinal fluid through lumbar puncture or performing expensive PET scans. These invasive or costly methods are difficult to implement on a large scale at the population level. Therefore, the true prevalence of Alzheimer's disease has remained a mystery. Dag Aarsland and colleagues innovatively used a non-invasive blood test method - detecting the level of phosphorylated tau protein (at the Thr217 site) in plasma - as a biomarker for ADNC (Alzheimer's disease neuropathological changes). The researchers analyzed 11,486 blood samples from volunteers aged 57 and older from the Trøndelag Health Study in Norway.
The results were surprising: the prevalence of ADNC increased significantly with age. In the 58-69.9 age group, the prevalence was less than 8%; while in the over-90 age group, this proportion soared to 65.2%. This data indicates that the burden of Alzheimer's disease-related pathology in the elderly population is far greater than previously estimated.
Pathological Changes Also Found in Cognitively Normal Individuals
The researchers further conducted a stratified analysis of individuals over 70 years old: 1) Among dementia patients, 60% had ADNC; 2) In individuals with mild cognitive impairment, this proportion was 32.6%; 3) And even in cognitively normal individuals, 23.5% still tested positive for ADNC.
This means that Alzheimer's disease pathological changes are not only present in those who have already developed the disease; a considerable number of seemingly healthy elderly people are actually in a "pathological incubation period". This also explains why the brain has already undergone subtle changes in some people before obvious symptoms appear. At the same time, researchers also found that people with higher levels of education have a relatively lower incidence of ADNC, suggesting that education and cognitive reserve may have a protective effect in delaying the pathological process.
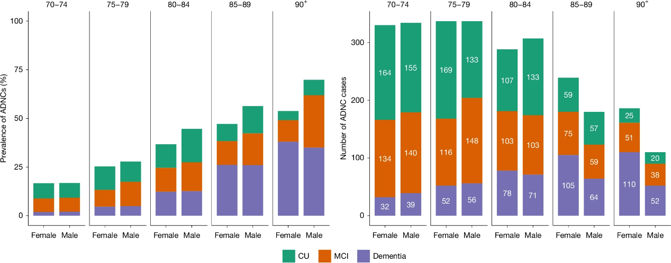
Alzheimer's Disease is Not "Female-Dominated"
For a long time, Alzheimer's disease has been considered a "female-dominated" disease, with women generally thought to have a higher incidence than men. However, this large-scale study overturned this view-researchers found no significant gender differences across all age groups.
This finding reminds us that the risk factors and disease progression of Alzheimer's disease may be more complex than previously thought, and previous conclusions about gender differences based on clinical samples may have been influenced by multiple factors such as access to healthcare and psychosocial factors.
Early Screening and Precise Intervention Become Possible
In addition, the study also yielded an exciting finding: in people over 70 years old, approximately 11% of participants met the eligibility criteria for monoclonal antibody treatment. These new drugs can slow cognitive decline, but they require precise timing and patient selection. To address this global challenge, it is essential to detect signs of dementia at the earliest stage, and this blood test appears to be an efficient means of providing clear information on a large scale. Although this blood test is not yet widely available in public healthcare systems, the research team has begun exploring the effectiveness of these blood biomarkers in predicting the development of dementia and plans to collaborate with primary care institutions to promote its practical application in primary care.
Creative Bioarray is the leading preclinical CRO specializing in animal models services. We have a wide range of transgenic and inducible mouse and rat models readily available for your studies. Our team of animal model scientists will work with you to find the right model.
Learn more about our fully characterized and validated animal models.
Reference:
- Aarsland, Dag, et al. "Prevalence of Alzheimer's disease pathology in the community." Nature (2025): 1-5.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *