Introduction on The Heterogeneity of Tumor Cell
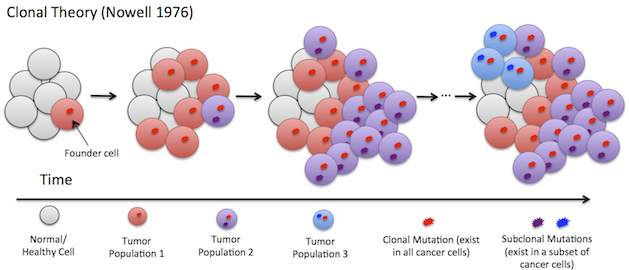
What is tumor heterogeneity? Tumor heterogeneity refers to the difference between genotype and phenotype of tumor cells in different parts of the same malignancy or in different parts of the same patient. Tumor heterogeneity refers to the difference between genotype and phenotype of tumor cells in different parts of the same malignancy or in different parts of the same patient. This difference can occur in different individuals, which can show different genetic backgrounds such as chromosome mass and quality differences, different cell types. There are also significant differences homogeneous tumors at the molecular level, such as gene expression profile, network regulation, mutation spectrum and other aspects of the difference. The inconsistencies happen between the mutant gene spectrum and biological characteristics in the same tumor patient, reflecting a high degree of complexity and diversity for the evolution process of malignant tumors. The mechanism of tumor heterogeneity This heterogeneity can be traced back to normal human cells. With the development of single-cell whole genome sequencing technology, each cell in normal cells prove to be different, genome, phenotype, developmental stage and gene expression will cause the same tissue origin between a group of cells Heterogeneity. The origin of tumor heterogeneity Most common view for the origin of tumor heterogeneity is from cancer stem cells. Cancer stem cells refer to a small group of stem cell-like cells with infinite self-renewal ability in the tumor, which can evolve into different phenotypic cell populations with strong tumorigenicity. Affected by cell differentiation, clonal evolution and microenvironment and other factors, leading to phenotypic and functional heterogeneity. The maintenance of heterogeneity is related to randomness. The breast cancer cells were divided into three subgroups: stem cell-like subsets, basal cell subsets and bursal epithelial subgroups by flow cytometry. Keep culturing three subpopulations of cells, then each suboperation will produce another three subgroups, and there was a random conversion mechanism in the cells to maintain the balance of stem cell-like cells. Cell fusion may be a source of metastatic tumor cell heterogeneity. Using the breast cancer lines MDA-MB-231 and MA11 co-cultured with human normal bone-derived stromal pluripotent cells, the spontaneous fusion of heterozygous cells was observed and the DNA content was aneuploidy. The hybrid cells were inoculated into immunization Defective mice, breast tumors can be observed in metastatic capacity. Analysis of heterogeneity from the genetic perspective, tumor cell genetic material instability is one of the reasons, the tumor cells are aneuploid. While analyzing the colon cancer, three genes related to DNA replication, MCD4, MEX3C, and ZNF516, being found. The loss of the above-mentioned genes resulted in stress during DNA replication leading to the appearance of aneuploid and abnormal chromosomes, resulting in heterogeneous tumor cells. The Future Study of tumor heterogeneity In-depth study of tumor heterogeneity has contributed to analyzing the mechanism of tumor production and evolution of the law to explain the reason for the reactivity happening in the process of treatment. In recent years, the good efficacy of tumor immunotherapy has been greatly encouraged and highly regarded by the global researchers. In fact, how to choose the target of immune therapy is still the difficulty of treatment, not all tumors are suitable for immunotherapy with the tumor heterogeneity at work. Tumor heterogeneity of the tumor biomarker prediction also makes it become more difficult. But we believe that professional study on tumor cell heterogeneity will provide a more supportive basis for future cancer-related disease treatment! Related products tumor cells

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *