Embracing Extra Pounds: The Surprising Role of Leptin in Cancer Fighting!
Aging is a major risk factor for many cancers, with patients aged 65 and older accounting for 60% of newly diagnosed cancers. Aging leads to T cell immune remodeling, which contributes to poor clinical outcomes in cancer patients. During aging, T cells undergo age-dependent changes and gradually lose their physiological functions. Numerous studies have demonstrated that T cells mediate tumor surveillance and clearance, and various strategies have been developed to enhance tumor-specific T cell responses. However, these experimental studies have almost exclusively been conducted in young individuals, not elderly individuals (Unlock the secrets of aging with our specialized cells!). Therefore, how age-related T cell dysfunction affects anti-tumor immunity requires further investigation.
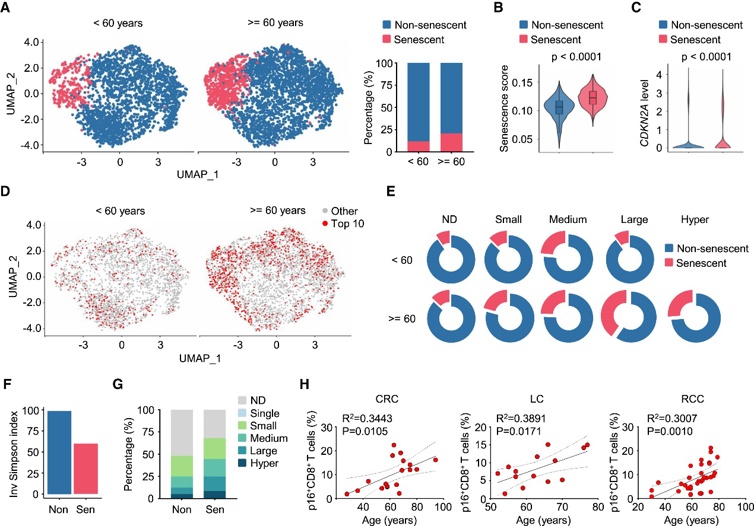
Age-related T cell dysfunction is driven by the molecular hallmarks of aging, resulting in a breakdown of cellular and physiological integrity. Indeed, genomic instability, epigenetic alterations, metabolic dysfunction, cellular senescence, and other biological defects can all contribute to T cell senescence. Among the many hallmarks of aging, changes in cellular and systemic metabolism have a profound impact on T cell function and phenotype.
Aging leads to defects in T cell mitochondrial function and limits their anti-tumor function. In addition to T cell-intrinsic mechanisms, aging also mediates systemic metabolic changes that impair T cell responses to cancer. Although age-related metabolic disturbances interfere with anti-tumor T cell responses, further research is needed to determine the interplay between age-related metabolic dysfunction and T cell senescence in the tumor microenvironment (TME).
One way our bodies regulate weight is through the use of leptin, a hormone produced by adipose tissue. The more adipose tissue in the body, the more leptin is produced. Leptin reaches the brain and "informs" specific neurons about the amount of fat stored in the body; high levels of leptin indicate high fat stores.
Recent studies have found that the decline in leptin levels with aging accelerates CD8+ T cell senescence, leading to T cell dysfunction in the tumor microenvironment. Adipocyte-derived leptin protects CD8+ T cell senescence in a p38-dependent manner.
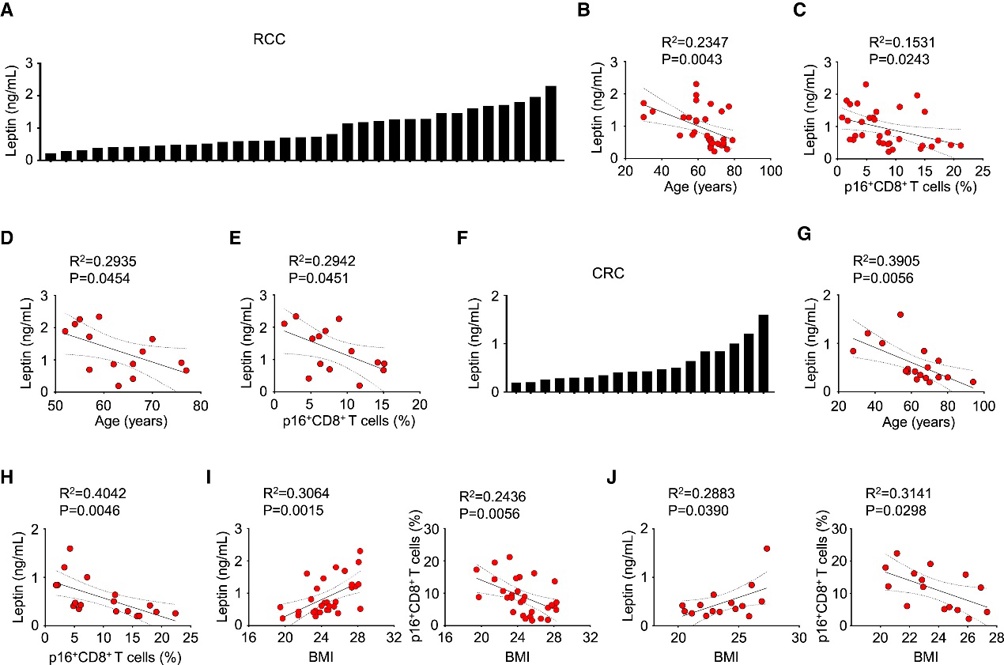
In human and mouse cancers, age-related decreases in systemic leptin levels contribute to CD8+ T cell senescence. Indeed, in human patients with colorectal, lung, or kidney cancer, plasma leptin levels are negatively correlated with the degree of CD8+ T cell senescence within tumors. Notably, in cancer patients, a higher body mass index (BMI) is associated with higher plasma leptin levels and a reduced proportion of senescent CD8+ T cells within tumors.
Collectively, these findings suggest that increasing plasma leptin levels by regulating adipocyte metabolism may be valuable for preventing T cell senescence and enhancing anti-tumor immunity in the elderly. These findings suggest that appropriate leptin supplementation may have therapeutic potential for elderly cancer patients.
Reference:
- Wang, Feixiang, et al. An age-related decrease in leptin contributes to CD8+ T cell aging in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Reports Medicine (2025).

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *