Cell Types in Bones
As we all know that the skeleton is a dynamic organ. The bone cells’ coordinated actions determine the shape and form of body. This post is used to express the cell types in bones.
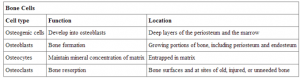
There are four types of cells in bone---osteocytes, osteoclasts, osteoblasts and osteoprogenitor cells. However, in different locations in bones, these cell types have different functions. Osteoblast, which is found in the growing portions of bone, including endosteum and periosteum, is responsible for forming new bone. These cells do not divide, synthesize and secrete the collagen matrix and calcium salts. With the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies, osteoblast becomes trapped within it. And then, its structure changes, becoming an osteocyte, which is the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell. With the help of secretion of enzymes, osteocytes can maintain the mineral concentration of the matrix.
 (resource:https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/the-musculoskeletal-system-38/bone-216/cell-types-in-bones-816-12058/images/bone-cell-types)
The most important cell is osteogenic cell, which is undifferentiated with high mitotic activity, is the only bone cells that are capable of dividing. It plays very crucial role when the function of mitosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes disappeared.
As for the osteoclasts, they continually break down old bone when osteoblast cells are forming new bone. This function is really necessary in maintenance, repair and remodelling of bones of the vertebral skeleton.
These are main four types of bone cells in skeleton. To know more information about this is very significant for us to study some bone diseases.
Other related product
Human Osteoblasts (HOB)
(resource:https://www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/the-musculoskeletal-system-38/bone-216/cell-types-in-bones-816-12058/images/bone-cell-types)
The most important cell is osteogenic cell, which is undifferentiated with high mitotic activity, is the only bone cells that are capable of dividing. It plays very crucial role when the function of mitosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes disappeared.
As for the osteoclasts, they continually break down old bone when osteoblast cells are forming new bone. This function is really necessary in maintenance, repair and remodelling of bones of the vertebral skeleton.
These are main four types of bone cells in skeleton. To know more information about this is very significant for us to study some bone diseases.
Other related product
Human Osteoblasts (HOB)

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *